Search Results for: external respiration
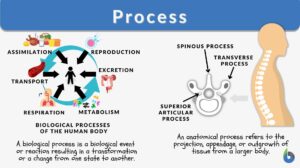
Respiration
Definition noun, plural: respirations Any of the various analogous processes by which there is an exchange of... Read More
An introduction to Homeostasis
Researched and Written by Jonjo MinnsSubmitted to biologyonline.com on February 25, 2009.Published in biologyonline.com... Read More
External Respiration
The bodily process of inhalation and exhalation; the process of taking in oxygen from inhaled air and releasing carbon... Read More
Muscular system
Muscular System Definition What is the muscular system? The muscular system is a system that includes muscle cells and... Read More
Respiration
Organization of the Respiratory System Each lung is composed of air sacs called alveoli - the sites of gas exchange with... Read More
Mitochondrion
Mitochondrion Definition What are mitochondria? The term “mitochondrion” comes from the two words of the Greek... Read More
Animal Water Regulation
Homeostatic control, a set environment, and how evolution and natural selection drives a species to adapt to its environment... Read More
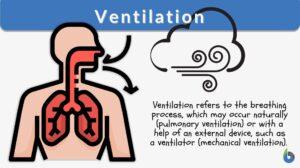
Ventilation
Ventilation Definition Often when persons think of ventilation, they think of getting clean or enough air into a room. This... Read More
Plasma membrane
Do all cells have a plasma (or cell) membrane? Yes, all cells have a biological membrane that separates the protoplasm from... Read More
Still Water Community Plants
Freshwater Plants & Water As mentioned in the previous tutorial about still water plants, the method of transpiration... Read More
Equilibrium
Equilibrium Definition In Biology Equilibrium refers to the state of balance and stability. In biology, equilibrium is... Read More
Water in Plants
The movement of molecules, specifically water and any solutes, is vital to understand in light of plant processes. This will... Read More
Eubacteria
Eubacteria are prokaryotic microorganisms consisting of a single cell lacking a nucleus and containing DNA is a single... Read More
Light-dependent reaction
Many organisms, such as green plants, convert light energy into chemical energy through the mechanism of photosynthesis. In... Read More
Assimilation
Assimilation Definition What is assimilation? Assimilation in biology is defined as the process in which living organisms... Read More
Parenchyma
Parenchyma Definition What does parenchyma mean? Let's define the word "parenchyma". Most of the functional tissues in... Read More
Genetic Control – On and Off Genes
Reviewed by: Mary Anne Clark, Ph.D.This lesson looks at the various factors involved that affect growth and... Read More
Biological Cell Introduction
It only takes one biological cell to create an organism. In fact, there are countless species of single-celled organisms,... Read More
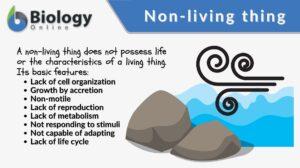
Non-living thing
Non-living Thing Definition A non-living thing in biology means any form without a life, such as an inanimate body or... Read More
Plant Water Regulation
A plant requires water as an essential ingredient of photolysis, the photochemical stage of photosynthesis where water is... Read More
Fruits, Flowers, and Seeds
Flowering plants grow in a wide variety of habitats and environments. They can go from germination of a seed to a mature... Read More
Fluid mosaic model
Fluid Mosaic Model Definition What is the fluid mosaic model? The fluid mosaic model is a three-dimensional representation... Read More
Phosphorylation
Phosphorylation Definition We can define phosphorylation as a biochemical process in which a phosphate molecule is added to... Read More
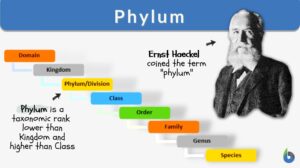
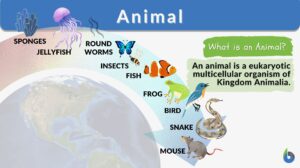
Kingdom Animalia
Kingdom Animalia Definition Each person can say that they know of or can name at least one animal. However, do people know... Read More
Selectively-permeable membrane
Selectively Permeable Membrane Definition We can define selectively permeable membranes as those that are selectively... Read More
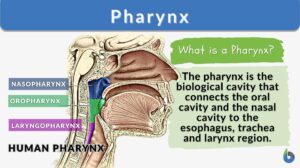
Digestion and Absorption of Food
The gastrointestinal (GI) system includes the gastrointestinal tract (mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine,... Read More
Concentration gradient
What is a concentration gradient? A gradient is a measure of how steep a slope is. Thus, a concentration gradient would be... Read More